基本类型占空间的大小 直接上例子:测试环境是64位机上。以下测试都在64位机上进行。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 #define sz(A) sizeof(A) int main () cout << "sz(int) = " << sz(int ) << endl ; cout << "sz(long) = " << sz(long ) << endl ; cout << "sz(long long) = " << sz(long long ) << endl ; cout << "sz(float) = " << sz(float ) << endl ; cout << "sz(double) = " << sz(double ) << endl ; cout << "sz(long double) = " << sz(long double ) << endl ; cout << "sz(char *) = " << sz(char *) << endl ; }
枚举类型和共用体类型占空间大小 枚举类型所占的空间是4字节。共用体中的所有成员共用的是同一段内存,共用体中的成员的偏移量也都一样,union所占的内存大小是最长的成员所占内存的大小,同时也要考虑到字节对齐,字节对齐遵循的原则是union变量的大小需要是最长成员(基本类型)大小的整数倍。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 #define sz(A) sizeof(A) int main () enum { a = 1 , b = 2 , m = 3 , ch = 'a' }_enum_A; union { char array [10 ]; char *p; }_union_U; cout << "sz(_enum_A) = " << sz(_enum_A) << endl ; cout << "sz(_union_U) = " << sz(_union_U) << endl ; printf ("%d\n" , (char *)&_union_U.p - (char *)&_union_U); }
类所占空间的大小 类中的函数不占空间,函数在代码区存放。如果一个类只含有函数(非虚函数),这个类占的内存大小是1,如果含有虚函数,就需要存放虚表指针,占用的空间是指针所占空间的大小。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 #define sz(A) sizeof(A) class A {public : int add (int a, int b) return a + b; } int fun () }; class B :public A { virtual int getSum () 0 ; virtual void print () virtual void fun () }; int main () cout << "sz(A) = " << sz(A) << endl ; cout << "sz(B) = " << sz(B) << endl ; }
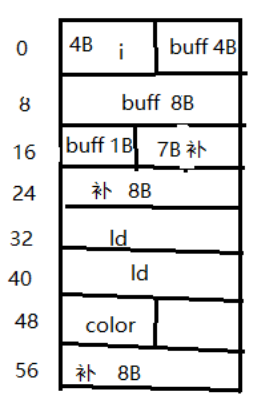
分析一下类所占内存大小和类中成员的偏移量。
成员的偏移量是该成员所占字节的整数倍,如果成员是结构体的话,那就是结构体中最长的基本类型所占字节的整数倍
类或结构体的总大小需要是类或结构体中最长的基本类型所占字节的整数倍
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 class Base { public : int i; union U { char buff[13 ]; int i; }u; long double ld; void foo () typedef char * (*f)(void *); enum {red, green, blue} color; } base; int main () cout << "sz(base) = " << sz(base) << endl ; cout << "The offset of ld is " ; printf ("%d\n" , (char *)&base.ld - (char *)&base); cout << "The offset of u is " ; printf ("%d\n" , (char *)&base.u - (char *)&base); }
全局变量和静态变量的存储是放在一块的,在程序编译时分配。局部类中不能包含静态变量,而全局类中可以包含静态变量,如果类中含有静态变量时,在用sizeof去统计类的大小时,静态变量不包含在内。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 class AA {public : int a; static int si; static struct { int abc; double d; }s; }; int main () cout << sz(AA) << endl ; }